Since the heart and lung positions are very close to the irradiation target area, protecting the heart and lung has always been an important consideration in breast radiotherapy. As seen from the anatomic relationship, the lungs are close to the chest wall, the heart is just in front of the left chest wall, and the inner side of the left chest wall is close to the front wall of the heart, with short distance to the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD). This anatomic structure easily makes the heart and lungs over-irradiated, thus inducing the risk of cardiovascular disease and radiation pneumonia.
Taking the left breast as an example, according to a study published in New England Medicine, the probability of cardiovascular disease increases by 7.4% for each growth of 1 GY radiation to the heart. There is a linear relationship between radiation-induced cardiac disease and cardiac radiation dose. When radiotherapy is applied to left breast cancer, the risk of radiation to the heart is one of the important factors that are highly concerned by the radiation therapist.
Prone Patient Immobilization Solution
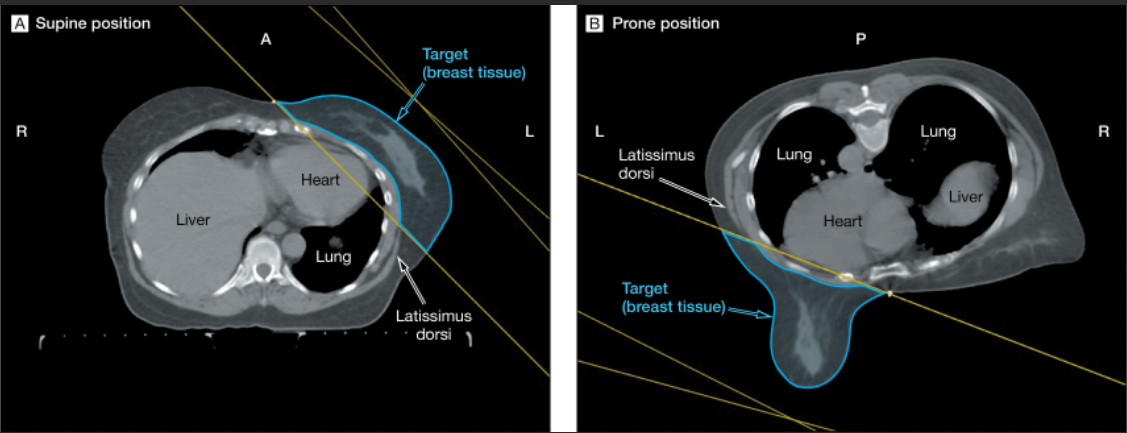
The breast-prone position was initially designed to be applied to patients with large breasts to solve the problem of excessive skin dose caused by skin folds in the supine position. With the deepening of clinical application research, some researchers found that the sagging of breasts caused by their gravity can widen the distance between the target area and the heart and lungs, which is conducive to avoiding the irradiation path of the beam and thus reducing the irradiation volume of the heart and lungs[1]
Fixation Solution
Cases are collected from Klarity
Patient Immobilization Solution
Baseplate:R612-AE4
Vacuum Bag:R7652-28NL-O
Clinical effect
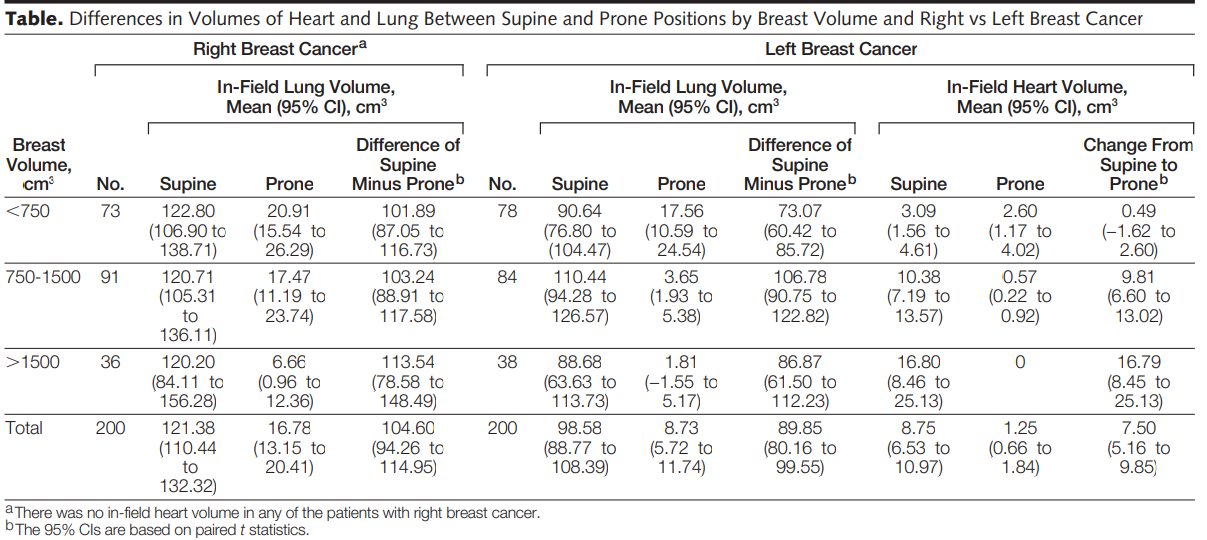
Silvia C.1.1 Formenti et al. conducted a retrospective study on 400 patients who received radiotherapy for left or right breast cancer from November 15th, 2005, to December 26th, 2008, in the Department of Radiation Oncology of New York University. The selected samples were 200 patients in supine and prone positions, respectively. The results showed that compared with supine position, the lung irradiation dose of patients with left and right breast cancer who received prone position radiotherapy decreased by 91.1% and 86.2% on average, and the heart irradiation dose of left breast cancer patients also decreased by 85.7% on average.[1]
Patient Immobilization operation skills
Using a wedge block to raise the chest wall of the unaffected side, the sagging effect of the affected side breast is better;
The tolerance of patients in a prone position is not good, and it is easy to cause large setup errors. Using a vacuum bag can increase the contact surface between the patient and the fixed board, thus improving comfort and setup precision.
References
[1] HFormenti, S. C., DeWyngaert, J. K., Jozsef, G., & Goldberg, J. D. (2012). Prone vs Supine Positioning for Breast Cancer Radiotherapy. JAMA, 308(9), 861.
[2] Tötterman KJ, Pesonen E, Siltanen P. Radiation-related chronic heart disease. Chest. 1983 Jun;83(6):875-8. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.6.875. PMID: 6851689.
[3] Yusuf SW, Sami S, Daher IN. Radiation-induced heart disease: a clinical update. Cardiol Res Pract. 2011 Feb 27;2011:317659. doi: 10.4061/2011/317659. PMID: 21403872; PMCID: PMC3051159.
[4] Duma MN, Baumann R, Budach W, Dunst J, Feyer P, Fietkau R, Haase W, Harms W, Hehr T, Krug D, Piroth MD, Sedlmayer F, Souchon R, Sauer R; Breast Cancer Expert Panel of the German Society of Radiation Oncology (DEGRO). Heart-sparing radiotherapy techniques in breast cancer patients: a recommendation of the breast cancer expert panel of the German society of radiation oncology (DEGRO). Strahlenther Onkol. 2019 Oct;195(10):861-871. English. doi: 10.1007/s00066-019-01495-w. Epub 2019 Jul 18. PMID: 31321461.
[5] Kahán Z, Rárosi F, Gaál S, Cserháti A, Boda K, Darázs B, Kószó R, Lakosi F, Gulybán Á, Coucke PA, Varga Z. A simple clinical method for predicting the benefit of prone vs. supine positioning in reducing heart exposure during left breast radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 2018 Mar;126(3):487-492. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.12.021. Epub 20
(Author: Wu Jiasheng, Pan Yulong)